At Lhasa we know that there are many challenges involved in carrying out risk assessments for drug substances and drug products, to ultimately ensure a safe and effective product for patients.
Forced degradation studies are essential in pharmaceutical development to assess drug stability and ensure product quality and safety. These studies help identify degradation pathways, support method development, validate stability-indicating methods, and troubleshoot stability issues. The collected degradation data informs formulation, packaging, storage conditions, and shelf life decisions for the drug product.
Establishing potential degradation products of a drug substance through forced degradation studies is outlined in guidelines (ICH Q1A and RDC 964/2025), though specifics on execution and stress conditions are left general. Designing these studies requires consideration of various factors, particularly the drug substance’s physicochemical properties. Stress testing typically begins in the preclinical phase and is repeated during clinical development alongside stability studies. Due to the complexity of organic reactions and pharmaceutical environments, identifying degradation mechanisms and control strategies is challenging. In silico tools can aid early in drug development by predicting reactivity risks and guiding experimental stress testing interpretation.
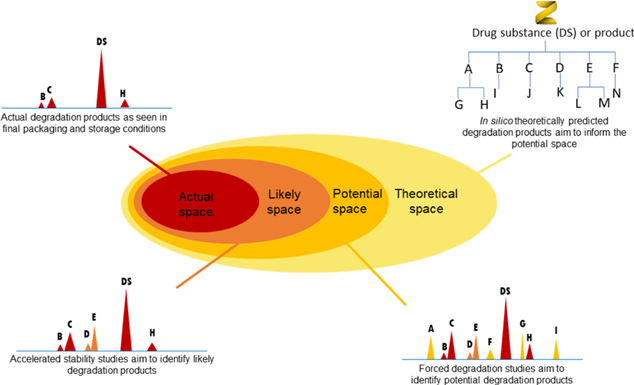
Image: Knowledge of the theoretical space from an in silico prediction can be used to support identification of degradation products, which will ultimately be observed in final packaging and storage conditions (the actual space). View the open access publication by Hemingway et al.
How can we help you overcome the challenges in forced degradation studies?
Zeneth is one such tool that can help analytical chemists to solve several challenges when conducting these studies, including:
1. Selection of Stress Conditions
The Challenge
Selecting appropriate stress conditions that reflect real-world degradation without over-stressing the API is a delicate balance. Overly harsh conditions can degrade too much of the API, while not degrading the sample enough may result in potential impurity formation being missed.
How Zeneth Helps
Zeneth allows chemists to input and save their condition sets for in silico predictions of the API and drug product to give an overview of the degradation chemistry expected under those conditions. Zeneth can provide:
- Prediction of likely degradation pathways under different stress conditions.
- Scientific rationale of the mechanism of degradation across the various conditions.
- Early identification of potential stability issues.
2. Identification of Degradation Products
The Challenge
Complex analytical techniques like HPLC and LC-MS/MS are required to identify and characterise the degradation products formed during forced degradation experimental studies, especially those present in trace amounts. This process can be time-consuming and resource intensive. A good knowledge of the expected chemistry is required to be able to elucidate the structures that correspond to the peaks seen in chromatography.
How Zeneth Helps
Zeneth supports degradation product identification by:
- Predicting an overview of potential degradation chemistry,
- Providing structural information for expected degradants, which is especially helpful when an impurity is present above the threshold for investigation.
- Helping prioritise which compounds to look for in analytical studies by providing likelihood scores.
- Reducing the time needed for structural elucidation by using the mass and/or (sub)structure filters.
3. Method development
The Challenge
A stability indicating method is an analytical procedure used to quantify the decrease in the amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in the drug product due to degradation. The method needs to include forced degradation experiments, method development and optimisation, and method validation.
Analytical chemists are required to develop a stability indicating method capable of separating the API from its degradation products. Some degradation products may have similar properties, such as retention time. For example, if an impurity arises that coelutes with the API peak in the chromatogram, the method will have failed, resulting in a waste of the batch and delay to market for the drug product.
The development of a suitable stability indicating method provides a background for the pre-formulation studies, stability studies, and the development of proper storage requirements.
How Zeneth Helps
By using Zeneth to help identify and characterise degradants found in experimental forced degradation studies, analytical chemists can design and troubleshoot a stability indicating method.
- The degradants generated from a forced degradation study are used as a sample to develop the stability indicating method. It is important that we can identify all degradation products accurately, which Zeneth can assist with.
- Zeneth can help to define an endpoint for the experimental studies so that the method is well defined to see all the possible degradation chemistry.
- Using Zeneth to assist in the identification of the chemical structures of degradants, along with their properties, will help in adjusting chromatography methods to ensure degradation products can be separated and identified.
4. Formulation components
The Challenge
It is important to ensure that the API and excipients are compatible to avoid both the generation of potentially toxic impurities and cosmetically undesirable reactions that will alter the appearance of the drug product when stored. It is also important to be aware of the impurities in the selected excipients, and the potential reactivity of these impurities with the API
How Zeneth Helps
- Zeneth doesn’t just assess APIs alone, it can also assess potential API-excipient interactions. We currently have a database of hundreds of excipients and their known impurities and contaminants. It is also possible to store your formulations (API and as many excipients as you require) in the software to run in silico predictions against multiple condition sets.
- Zeneth will also highlight any potential interactions between impurities present in excipients and the API. This is particularly relevant when the impurity is nitrite as this can lead to the formation of nitrosamines. Zeneth is aligned with the excipient data in Vitic Nitrites. (For more information on our data sharing initiatives head to our data sharing page.)
5. Regulatory submissions
The Challenge
Those submitting applications under international (ICH) guidelines and those submitting to Anvisa under the updated RDC 964/2025 guideline will know that thorough documentation and scientific justification for chosen methods and stress conditions will be required.
How Zeneth Helps
Zeneth supports regulatory acceptance by providing scientific justification across multiple stages of the drug-development process as outlined in the previous points of this blog.
- Documentation of predicted degradation pathways.
- Support for method development justification.
- Structural information for impurity qualification.
Forced degradation studies are a fundamental part of pharmaceutical development, helping to ensure drug stability, efficacy, and regulatory compliance. However, the process can be complex, time-consuming, and resource intensive. By leveraging in silico tools like Zeneth, chemists can streamline their workflows, optimise method development, and support regulatory submissions.
Contact our team to learn more about how Zeneth can support you.
Last Updated on March 27, 2025 by lhasalimited